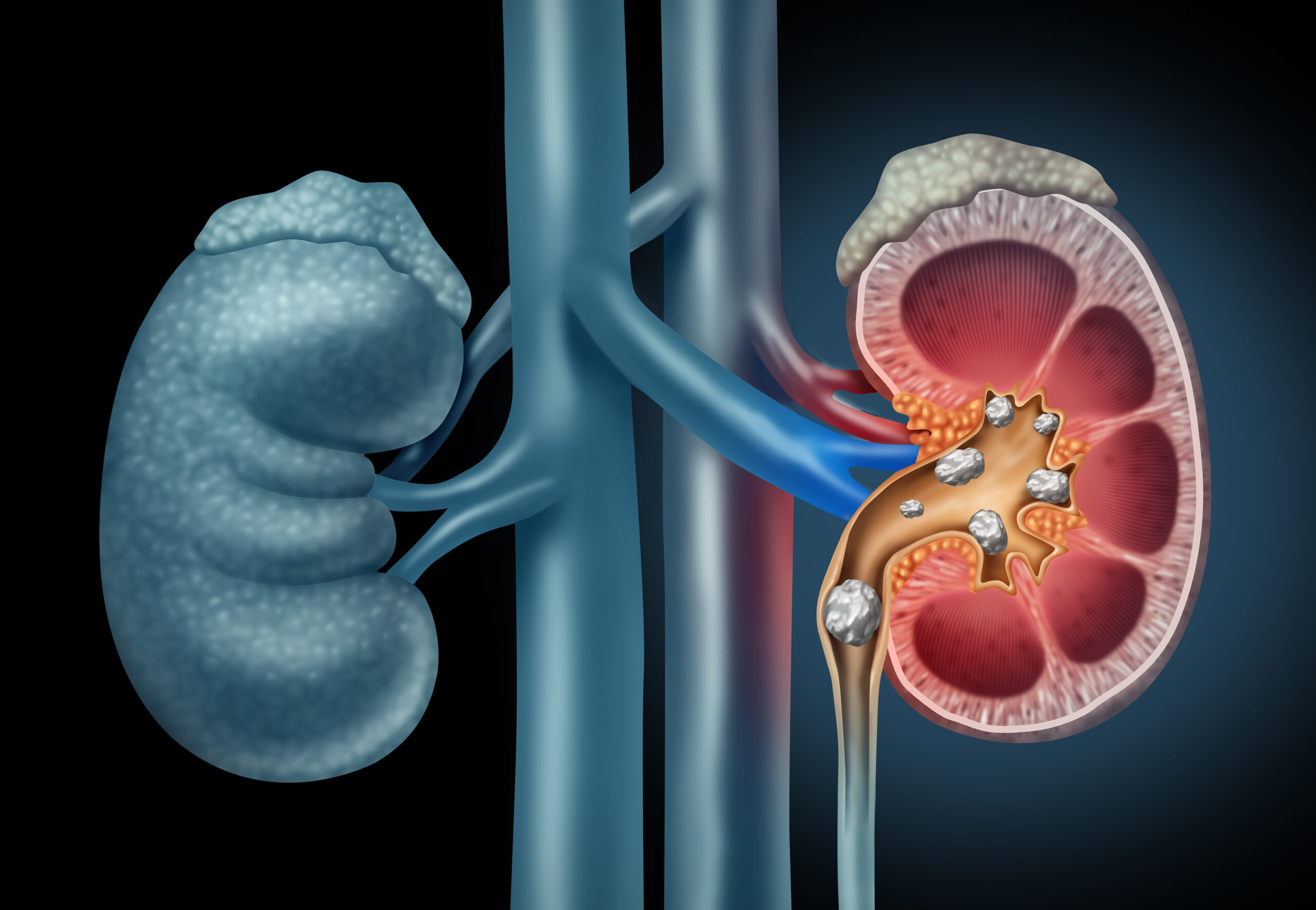
Kidney stones can be incredibly painful, but with a little knowledge, you can better understand them, take steps to prevent them, and even manage them if they occur. So, let’s discuss a little about them.
What Are Kidney Stones?
Kidney stones are solid, pebble-like structures that form in your kidneys. They are composed of minerals and salts that, over time, accumulate and crystallize. These stones can range in size from as small as a grain of sand to as large as a golf ball. When small, they can often pass out of the body unnoticed. However, larger stones can cause significant pain and complications.
Symptoms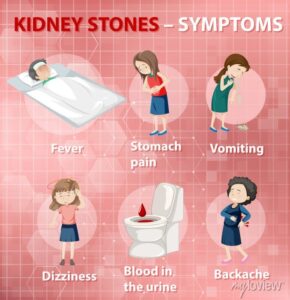
The symptoms of kidney stones can be quite distinctive. You might experience:
Intense Pain: One of the most common and excruciating symptoms is a sudden, severe pain in the back or side, often radiating to the lower abdomen and groin. This pain is often referred to as “renal colic.” It can be associated with nausea and vomiting.
Blood in Urine: Kidney stones can cause blood to appear in your urine, turning it pink, red, or brown.
Frequent Urination: You might find yourself needing to urinate more frequently or urgently.
Cloudy or Foul-Smelling Urine: Kidney stones can sometimes lead to changes in the appearance and odor of your urine.
Causes
Understanding what causes kidney stones can help you take steps to prevent them. Some common factors include:
Dehydration: Insufficient fluid intake can lead to concentrated urine, making it easier for stones to form.
Diet: Consuming too much salt, protein, or certain foods high in oxalates (like spinach and chocolate) can increase the risk.
Family History: If someone in your family has had kidney stones, you may be more prone to them.
Certain Medical Conditions: Conditions like obesity, high blood pressure, and inflammatory bowel disease can increase the risk of kidney stones.
Treatment and Prevention
If you suspect you have kidney stones or have experienced symptoms, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional. He will examine you and advice you some blood and urine tests and an ultrasound examination.
Here are some common approaches to treatment and prevention:
Hydration: Drink plenty of water to help flush out your urinary system and prevent stone formation.
Dietary Changes: Adjust your diet to reduce oxalate-rich foods and limit salt intake.
Medication: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help expel stones down or manage symptoms.
Medical Procedures: Larger stones might require medical procedures like shock wave lithotripsy or surgical removal.
Conclusion
While kidney stones can be incredibly painful, understanding their causes, symptoms, and prevention strategies can help you manage this condition effectively. If you suspect you have kidney stones, don’t hesitate to seek medical attention. With the right care and lifestyle adjustments, you can reduce your risk and enjoy a healthier, stone-free life. Remember, prevention is always better than cure!